自由扩展你的项目 - Builder模式
Builder 模式是一步一步创建一个复杂对象的创建型模式,它允许用户在不知道内部构建细节的情况下,可以更精细地控制对象的构造流程。该模式是为了将构建复杂对象的过程和它的部件解耦,使得构建过程和部件的表示隔离开来。
因为一个负载的对象又很多大量组成部分,如汽车,有车轮、方向盘、发动机,还有各种小零件等,如何将这些部件装配成一辆汽车,这个装配过程很漫长,也很复杂,对于这种情况,为了在构建过程中对外部隐藏实现细节,就可以使用Builder 模式将部件和组装过程分离,使得构建过程和部件都可以自由扩展,两者之间的耦合也降到最低。
# Builder 模式的定义
将一个复杂对象的构建与它的表示分离,使得同样的构建过程可以创建不同的表示。
# Builder 模式的使用场景
- 相同的方法,不同的执行顺序,产生不同的事件结果。
- 多个部件或零件,都可以装配到一个对象中,但是产生的运行结果又不相同时。
- 产品类非常复杂,或者产品类中的调用顺序不同产生了不同的作用,这个时候使用建造者模式非常合适。
- 当初始化一个对象特别复杂,如参数多,且很多参数都具有默认值时。
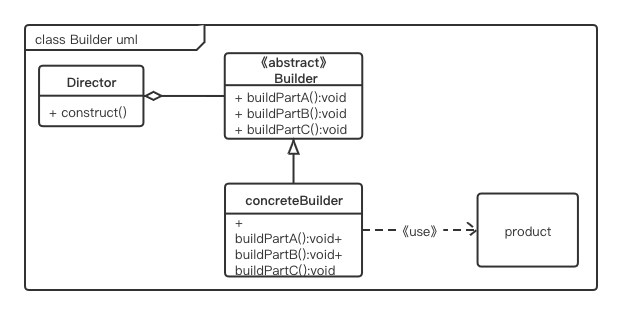
# Builder 模式的UML类图
UML 类图如图3-1所示。
角色介绍:
- Product 产品类 --- 产品的抽象类
- Builder --- 抽象Builder类,规范产品的组件,一般是由子类实现具体的组件过程
- ConcreteBuilder --- 具体的Builder类
- Director --- 统一组装过程
# Builder 模式的简单实现
计算机的组装过程较为复杂,并且组装顺序是不固定的,为了易于理解,我们把计算机组装的过程简化为构建主机、设置操作系统、设置显示器3个部分,然后通过Director和具体的Builder来构建计算机对象。请看下面的示例:
package com.dp.example.builder
//计算机抽象类,即Product角色
public abstract class Computer {
protected String mBoard;
protected String mDisplay;
protected String mOS;
protected Computer() {
}
//设置CPU核心数
public void setBoard(String board) {
mBoard = board;
}
//设置内存
public void setDisplay(String display) {
mDisplay = display;
}
//设置操作系统
public abstract void setOS();
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Computer [mBoard=" + mBoard + ", mDisplay=" + mDisplay + ", mOs=" + mOS + "]" ;
}
}
//具体的Computer 类, MacBook
public class Macbook extends Computer {
protected Macbook() {
}
@Overrid
public void setOS() {
mOS = "Mac OS X 10.10";
}
}
//抽象Builder 类
public abstract class Builder {
//设置主机
public abstract void buildBoard(String board);
//设置显示器
public abstract void buildDisplay(String display);
//设置操作系统
public abstract void buildOS();
//创建Computer
public abstract Computer create();
}
//具体的Builder类,MacbookBuilder
public class MacbookBuilder extends Builder {
private Computer mComnputer = new Macbook();
@Override
public void buildDisplay(String display) {
mComputer.setDisplay(display);
}
@Override
public void buildBoard(String board) {
mComputer.setBoard(board);
}
@Override
public void buildOS() {
mComputer.setOS();
}
@Override
public Computer create() {
return mComputer;
}
}
//Director类,负责构造Computer
public class Director {
Builder mBuilder = null;
/**
* @param builder
*/
public Director(Builder builder) {
mBuilder = builder;
}
/**
* 构建对象
*/
public void construct(String board, String display) {
mBuilder.buildBoard(board);
mBuilder.buildDisplay(display);
mBuilder.buildOS();
}
}
//测试代码
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//构建起
Builder builder = new MacbookBuilder();
//Director
Director pcDirector = new Director(builder);
//封装构建过程,4核、内存2GB、Mac系统
pcDirector.construct("英特尔主板", "Retina 显示器");
//构建计算机,输出相关信息
System.out.println("Computer Info:" + builder.create().toString());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
输出结果:
Computer Info: Computer [mBoard=英特尔主板, mDisplay=Retina 显示器, mOs=Mac OS X 10.10]
上述示例中,通过具体的 MacbookBuilder 来构建 Macbook对象,而Director封装了构建复杂产品对象的过程,对外隐藏构建细节。Builder与Director一起将一个复杂对象的构建与它的表示分离,使得同样的构建过程可以创建不同的对象。
值得注意的是,在显示开发过程中,Director 角色经常会被省略。而直接使用一个Builder 来进行对象的组装,这个Builder通常为链式调用,它的关键点是每个setter方法都返回自身,也就是 return this,这样就使得setter方法可以链式调用,代码大致如下:
new TestBuilder().setA("A").setB("B").create();
通过这种形式不仅去除了Director角色,整个结构也更加简单,也能对Product对象的组装过程更精细的控制。
# Android 源码中的Builder模式实现
在Android源码中,最常用到的Builder 模式就是AlertDialog.Builder,使用该Builder来构建复杂的AlertDialog对象。在开发过程中,我们经常用到AlertDialog,具体示例如下:
//显示基本的AlertDialog
private void showDialog(Context context) {
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new Alert.Builder(context);
builder.setIcon(R.drawable.icon);
builder.setTitle("title");
builder.setMessage("Message");
builder.setPositiveButton("Button1"), new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
setTitle("点击了对话框上的Button1");
}
};
builder.setNeutralButton("Button2"), new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
setTitle("点击了对话框上的Button2");
}
};
builder.setNegativeButton("Button3"), new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int whichButton) {
setTitle("点击了对话框上的Button3");
}
};
builder.create().show(); //构建AlertDialog,并且显示
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
从类名就可以看出这就是一个Builder模式,通过Builder对象来组装Dialog的各个部分,如title、buttons、Message等,将Dialog的构造和表示进行分离。下面看看AlertDialog的相关源码:
//AlertDialog
public class AlertDialog extends Dialog implements DialogInterface {
//AlertController 接收 Builder成员变量P中的各个参数
private AlertController mAlert;
//构造函数
protected AlertDialog(Context context, int theme) {
this(context, theme, true);
}
//构造AlertDialog
AlertDialog(Context context, int theme, boolean createContextWrapper) {
super(context, resolveDialogTheme(context, theme), createContextWrapper);
mWindow.alwaysReadCloseOnTouchAttr();
//构造AlertController
mAlert = new AlertController(getContext(), this, getWindow());
}
//实际上调用的是mAlert 的setTitle 方法
@Override
public void setTitle(CharSequence title) {
super.setTitle(title);
mAlert.setTitle(title);
}
//实际上调用的是mAlert的setCustomTitle方法
public void setCustomTitle(View customTitleView) {
mAlert.setCustomTitle(customTitleView);
}
public void setMessage(CharSequence message) {
mAlert.setMessage(message);
}
// AlertDialog 其他的代码省略
// ********** Builder 为AlertDialog的内部类 **********
public static class Builder {
//1. 存储AlertDialog 的各个参数,如title、message、icon等
private final AlertController.AlertParams P;
// 属性省略
public Builder(Context context) {
this(context, resolveDialogTheme(context, 0));
}
public Builder(Context context, int theme) {
P = new AlertController.AlertParams(new ContextThemeWrapper(
context,resolveDialogTheme(context. theme)));
mTheme = theme;
}
//2. 设置各种参数
public Builder setTitle(CharSequence title) {
P.mTitle = title;
return this;
}
public Builder setMessage(CharSequence message) {
P.mMessage = message;
return this;
}
public Builder setView(View view) {
P.mView = view;
P.mViewSpacingSpecified = false;
return this;
}
//3. 构建AlertDialog,传递参数
public AlertDialog create() {
//4. 调用new AlertDialog 构造对象, 并且将参数传递给个体AlertDialog
final AlertDialog dialog = new AlertDialog(P.mContext,mTheme, false);
//5. 将P中的参数应用到dialog 中的 mAlert对象汇总
P.apply(dialog.mAlert);
dialog.setCancelable(P.mCancelable);
if(P.mCancelable) {
dialog.setCancelableOnTouchOutside(true);
}
dialog.setOnCancelListener(P.mOnCancelListener);
if(P.mOnKeyListener != null) {
dialog.setOnKeyListener(P.mOnKeyListener);
}
return dialog;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
上述代码中,Builder类可以设置AlertDialog中的title、message、button 等参数,这些参数都存储在类型为AlertController.AlertParams的成员变量P中,AlertController.AlertParams中包含了与AlertDialog视图中对应的成员变量。在调用Builder类的create函数时会创建AlertDialog,并且将Builder成员变量P中保存的参数应用到AlertDialog 的mAlert 对象中,即P.apply(dialog.mAlert)代码段。我们再看看apply 函数的实现:
public void apply(AlertController dialog) {
if(mCustomTitleView != null) {
dialog.setCustomTitle(mCustomTitleView);
}else {
if (mTitle != null) {
dialog.setTitle(mTitle);
}
if (mIcon != null) {
dialog.setIcon(mIcon);
}
if (mIconId >= 0) {
dialog.setIcon(mIconId);
}
if(mIconAttrId > 0) {
dialog.setIcon(dialog.getIconAttributeResId(mIconAttrId));
}
}
if (mMessage != null) {
dialog.setMessage(mMessage);
}
if(mPositiveButtonText != null) {
dialog.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_POSITIVE, mPositiveButtonText, mPositiveButtonListener, null);
}
if(mNegativeButtonText != null) {
dialog.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_NEGATIVE, mNegativeButtonText, mNegativeButtonListener, null);
}
if(mNeutralButtonText != null) {
dialog.setButton(DialogInterface.BUTTON_NEUTRAL, mNeutralButtonText, mNeutralButtonListener, null);
}
if (mForceInverseBackground) {
dialog.setInverseBackgroundForced(true);
}
// 如果设置了mItems, 则表示是单选或者多选列表,此时创建一个ListView
if ((mItems !=null) || (mCursor != null) || (mAdapter !=null)) {
createListView(dialog);
}
//将mView设置给Dialog
if (mView != null) {
if (mViewSpacingSpecified) {
dialog.setView(mView, mViewSpacingLeft, mViewSpacingTop, mViewSpacingRight, mViewSpacingBottom);
} else {
dialog.setView(mView);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
在apply函数中,只是将AlertParams参数设置到AlertController中,例如,将标题设置到Dialog对应的标题视图中,将Message 设置到内容视图中等。当我们获取到AlertDialog 对象后,通过show函数就可以显示这个对话框。我们看看Dialog 的show函数(该函数在Dialog类中):
// 显示Dialog
public void show() {
//已经是显示状态,则return
if(mShowing) {
if (mDecor != null) {
if (mWindow.hasFeature(Window.FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) {
mWindows.invalidatePanelMenu(Window.FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
}
mDecor.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
return;
}
mCanceled = false;
//1. OnCreate 调用
if (!mCreated) {
dispatchOnCreate(null);
}
//2. onStart
onStart();
//3. 获取DecorView
mDecor = mWindow.getDecorView();
//代码省略
//4. 获取布局参数
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = mWindow.getAttributes();
if ((l.softInputMode & windowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_FORWARD_NAVIGATION) == 0) {
WindowManager.LayoutParams nl = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
nl.copyFrom(l);
nl.softInputMode = WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_FORWARD_NAVIGATION;
l = nl;
}
try {
// 5. 将mDecor 添加到 WindowManager 中
mWindowManager.addView(mDecor, 1);
mShowing = true;
//发送一个显示Dialog 的消息
sendShowMessage();
} finally {
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
在show 函数中 主要做了如下几个事情:
- 通过
dispatchOnCreate函数来调用AlertDialog 的onCreate函数; - 然后调用AlertDialog 的onStart 函数。
- 最后将Dialog 的DecorView 添加到WindowManager中。
很明显,这就是一系列典型的生命周期函数。那么按照惯例,AlertDialog的内容视图构建按理应该在onCreate函数中,我们来看看是不是:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(saveInstanceState);
//调用了AlertController 的installContent 方法
mAlert.installContent();
}
2
3
4
5
6
在onCreate函数中主要调用了AlertController的 installContent 方法,Dialog中的onCreate函数只是一个空实现而已,可以忽略它。那么AlertDialog的内容视图必然就在installContent函数中,继续深入了解吧:
public void installContent() {
/*设置窗口,没有Title */
mWindow.requestFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
//省略其他设置
//设置窗口的内容视图布局
mWindow.setContentView(mAlertDialogLayout);
//初始化AlertDialog 其他子视图的内容
setupView();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
installContent函数的代码很少,但极为重要,它调用了Window对象的setContentView,这个setContentView就与Activity中的一模一样,实际上Activity最终也是调用Window对象的setContentView 函数。因此,这里就是AlertDialog的内容布局,这个布局就是mAlertDialogLayout字段的值,这个值在AlertController 构造函数中进行了初始化,具体代码如下:
public AlertController(Context context, DialogInterface di, Window window) {
//代码省略
TypeArray a = context.obtainStyleedAttributes(null,
com.android.internal.R.styleable.AlertDialog,
com.android.internal.R.attr.alertDialogStyle, 0);
AlertDialogLayout = a.getResourceId(
com.android.internal.R.styleable.AlertDialog_layout,
com.android.internal.R.layout.alert_dialog);
//代码省略
a.recycle();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
从AlertController 的构造函数中可以看到,AlertDialog的布局资源就是alert_dialog.xml 这个文件,由于这个布局文件有点长,我们就不附上源代码,用下图来大致描述一下它的结构。
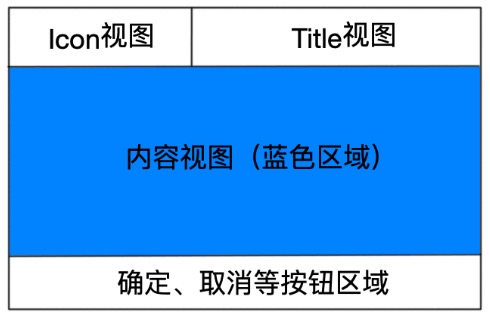
当通过Builder 对象的setTitle、setMessage 等方法设置具体内容时,就是将这些内容填充到对应的视图中。而AlertDialog也允许你通过setView传入内容视图,这个内容视图就是替换掉上图的蓝色区域,AlertDialog预留了一个costumePanel区域用来显示用户自定义的内容视图。我们来看看setupView函数:
private void setupView() {
//1. 获取并初始化内容区域
LinearLayout contentPanel = (LinearLayout)mWindow.findViewById(R.id.contentPanel);
setupContent(contentPanel);
//2. 初始化按钮
boolean hasButton = setupButton();
//3. 获取并初始化Title区域
LinearLayout topPanel = mWindow.findViewById(R.id.topPanel);
TypeArray a = mContext.obtainStyledAttributes(null,
com.android.internal.R.styleable.AlertDialog,
com.android.internal.R.attr.alertDialogStyle, 0);
boolean hasTitle = setupTitle(topPanel);
// 按钮区域的可见性
View buttonPanel = mWindow.findViewById(R.id.buttonPanel);
if (!hasButton) {
buttonPanel.setVisibility(View.GONE);
mWindow.setCloseOnTouchOutsideIfNotSet(true);
}
//4. 自定义内容视图区域
FrameLayout customPanel = null;
//如果用户设置了内容区域,那么将它显示在customPanel的custom布局里面
if (mView != null ){
customPanel = (FrameLayout)mWindow.findViewById(R.id.customPanel);
FrameLayout custom = mWindow.findViewById(R.id.custom);
//显示用户设置的视图
custom.addView(mView, new LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
if (mViewSpacingSpecified) {
custom.setPadding(mViewSpacingLeft, mViewSpacingTop, mViewSpacingRight, mViewSpacingBottom);
}
if (mListView != null) {
((LinearLayout.LayoutParams) customPanel.getLayoutParams()).weight = 0;
}
} else {
mWindow.findViewById(R.id.customPanel).setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
//代码省略
//设置北京
setBackground(topPanel, contentPanel, customPanel, hasButtons, a, hasTitle, buttonPanel);
a.recycle();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
这个setupView顾名思义就是初始化AlertDialog布局中的各个部分,如标题区域、按钮区域、内容区域等,在该函数调用之后整个Dialog的视图内容全部设置完毕。而这些各区域的视图都属于mAlertDialogLayout 布局中的子元素,Window对象又关联了mAlertDialogLayout的整个布局树,当调用完setupView之后整个视图树的数据都填充完毕,当用户调用show函数时,WindowManager会将Window对象的DecorView(也就是mAlertDialogLayout对应的视图,当然DecorView 还有一个层次,我们不做过多讨论)添加到用户的窗口上,并且显示出来。至此,整个Dialog就出现在用户的视野中了!
在AlertDialog的Builder模式中并没有看到Director角色的出现,其实在很多场景中,Android并没有完全按照GOF在《设计模式:可服用面向对象软件的基础》一书中描述的经典模式实现来做,而是做了一些修改,使得这个模式更易于使用。这里的ALertDialog.Builder 同时扮演来上文中提到的builder、ConcreteBuilder、Director的角色,简化来Builder模式的设计。当模块比较稳定,不存在一些变化时,可以在经典模式实现的基础上作出一些精简,而不是照搬GOF上的经典实现,更不要生搬硬套,使程序失去架构之美。正是由于灵活地运用设计模式,Android的源码很值得我们去学习。
# Builder模式实战
随着ImageLoader的不断演进,这个库的可扩展性、灵活性越来越高,在带来用户关注的同时也需要开发一些新特性来满足用户的需求,比较典型的问题就是配置ImageLoader,如缓存配置等,这还远远不够! 用户需要更大的灵活性,更多的定制化,如设置图片在加载时ImageView显示的图片、加载失败后显示的图片、图片加载引擎线程数等。
public class ImageLoader {
// 图片缓存
ImageCache mImageCache = new MemoryCache();
//图片加载中显示的图片id
int mLoadingImageId;
//图片加载失败时显示的图片id
int mLoadingFailedImageId;
//图片加载策略
LoaderPolicy mLoaderPolicy;
//线程池,线程数量为CPU的数量
ExecutorService mExecutorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(Runtime.
getRuntime().availableProcessors());
//省略单例模式部分代码
public void displayImage(String imageUrl, ImageView imageView) {
Bitmap bitmap = mImageCache.get(imageUrl);
if (bitmap != null) {
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
return;
}
//提交图片加载请求
submitLoadRequest(imageUrl, imageView);
}
public void setImageCache(ImageCache cache) {
mImageCache = cache;
}
public void setLoadingImage(int resId) {
mLoadingImageId = resId;
}
public void setLoadingFailedImage(int resId) {
mLoadingFailedImageId = resId;
}
public void setLoadingPolicy(LoaderPolicy policy) {
mLoaderPolicy = policy;
}
public void setThreadCount(int count) {
mExecutorService.shutDown();
mExecutorService = null;
//设置新的线程数量
mExecutorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(count);
}
private void submitLoadRequest(final String imageUrl, final ImageView imageView) {
//设置加载中的图片
imageView.setImageResource(mLoadingImageId);
imageView.setTag(imageUrl);
mExecutorService.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//加载图片
Bitmap bitmap = downloadImage(imageUrl);
if (bitmap == null) {
//设置加载图片失败后显示的图片
imageView.setImageResource(mLiadingFailedImageId);
return;
}
//显示加载到的图片
}
});
}
public Bitmap downloadImage(String imageUrl) {
Bitmap bitmap = null;
//省略下载图片的过程
return bitmap;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
这段代码就是创建对应的成员变量,然后通过setter方法来设置这些变量值,使得这些特性都能够被用户定制。看似很好用,代码简单、灵活性好,但是ImageLoader里的函数较多,且用户可以在任何时候修改ImageLoader的配置,这就出现了一个问题,如在已经初始化了一个指定线程数量的线程池的情况下,用户再调用setThreadCount时应该如何处理呢?而且这样的设计也使得用户的使用成本变高。里面过多的函数暴露,也让用户在每次调用函数时都要仔细选择,你能否对这个程序做一些限制,比如用户只能在初始化时配置这些参数?我们来看看知名图片加载库 Universal-Image-Loader 的初始化配置是怎么写的:
ImageLoaderConfiguration config = new ImageLoaderConfiguration.Builder(context)
.threadPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY - 2)
.denyCacheImageMultipleSizesInMemory()
.discCacheFileNameGenerator(new Md5FileNameGenerator())
.tasksProcessingOrder(QueueProcessingType.LIFO)
.writeDebugLogs() // Remove for release app
.build();
//初始化ImageLoader
ImageLoader.getInstance().init(config);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
“将一个复杂对象的构建与他的表示分离”,用Builder模式来构建一个不可变的配置对象,并且将这个配置对象注入到ImageLoader中,也就是说它只能在构建时设置各个参数,一旦你调用build()或者类似方法构建对象之后,它的属性就不可再修改,因为它没有setter方法,字段也都是隐藏的,用户只能在初始化时一次性构造这个配置对象,然后注入给ImageLoader,ImageLoader根据配置对象进行初始化。这样,上一个版本中的setThreadCount、setImageCache等方法就不需要出现在ImageLoader中了,用户可见的函数就会少很多,ImageLoader的使用成本也随之降低了。
我们看看修改后的ImageLoader,具体代码如下:
public final class ImageLoader {
//图片加载配置对象
private ImageLoaderConfig mConfig;
//省略单例模式的代码
/**
* 初始化ImageLoader
* @param config
*/
public void init(ImageLoaderConfig config) {
mConfig = config;
//检测配置的合法性,内部会根据配置做一些初始化操作
checkConfig();
//代码省略
}
//加载图片的函数
public void displayImage(String imageUrl, ImageView imageView) {
Bitmap bitmap = mImageCache.get(imageUrl);
if (bitmap != null) {
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
return;
}
// 添加加载请求
submitLoadRequest(imageurl, imageView);
}
private void submitLoadRequest(final String imageUrl, final ImageView imageView) {
//代码省略
}
public Bitmap downloadImage(String imageUrl) {
Bitmap bitmap = null;
//代码省略
return bitmap;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
上述代码中,把配置的代码基本上都封装到ImageLoaderConfig 和 Builder对象中,一起来看看相关代码:
public class ImageLoaderConfig {
//图片缓存配置对象
BitmapCache bitmapCache = new MemoryCache();
//加载图片时的loading 和加载失败的图片配置对象
DisplayConfig displayConfig = new DisplayConfig();
//加载策略
LoadPolicy loadPolicy = new SerialPolicy();
//线程数量,默认为CPU数量+1
int threadCount = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() + 1;
private ImageLoaderConfig() {
}
/**
* 配置类的Builder
*/
public static class Builder {
/**
* 图片缓存配置对象
*/
BitmapCache bitmapCache = new MemoryCache();
/**
* 加载图片时的loading和加载失败的图片配置对象
*/
DisplayConfig displayConfig = new DisplayConfig();
/**
* 加载策略
*/
LoadPolicy loadPolicy = new SerialPolicy();
//线程数量
int threadCount = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() +1;
//设置线程数量
public Builder setThreadCount(int count) {
threadCount = Math.max(1, count);
return this;
}
//设置缓存
public Builder setCache(BitmapCahce cache) {
bitmapCache = cache;
return this;
}
//设置图片加载中显示的图片
public Builder setLoadingPlaceholder(int resId) {
displayConfig.loadingResId = resId;
}
//设置图片加载失败时显示的图片
public Builder setNotFoundPlaceholder(int resId) {
displayConfig.failedResId = resId;
}
public Builder setLoadPolicy(LoadPolicy policy) {
if (policy != null) {
loadPolicy = policy;
}
return this;
}
void applyConfig(ImageLoaderConfig config) {
config.bitmapCache = this.bitmapCache;
config.displayConfig = this.displayConfig;
config.loadPolicy = this.loadPolicy;
config.threadCount = this.threadCount;
}
/**
* 根据已经设置好的属性创建配置对象
* @return ImageLoaderConfig对象
*/
public ImageLoaderConfig create() {
ImageLoaderConfig config = new ImageLoaderConfig();
//应用配置
applyConfig(config);
return config;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
通过将ImageLoaderConfig 的构造函数、字段私有化,使得外部不能访问内部属性,用户唯一能够设置属性的地方就是通过Builder对象了,也就是说用户只能通过Builder对象构造ImageLoaderConfig对象,这就是构建和表示相分离。
但是“使得相同的构造过程可以创建不同的表示” 又是如何理解呢? 在经典的Builder模式中还有一个Director 和ConcreteBuilder角色,不同的ConcreteBuilder是可以创建不同的Product子类的,因此,也就是可以创建不同的表示。我们这里并没有使用经典实现,因此,不做过多的描述。
我们来看看使用Builder模式重构后的ImageLoader如何使用:
private void initImageLoader() {
ImageLoaderConfig config = new ImageLoaderConfig.Builder()
.setLoadingPlaceholder(R.drawable.loading)
.setNotFoundPlaceholder(R.drawable.not_found)
.setCache(new DoubleCache(this))
.setThreadCount(4)
.setLoadPolicy(new ReversePolicy()).create();
//将配置初始化到ImageLoader中
ImageLoader.getInstance().init(config);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
调用init函数之后,ImageLoader就可以正常使用了,各种setter函数不会在用户调用ImageLoader方法时出现在视野中,他们已经被隔离到了Builder模式中。
# 总结
Builder模式在Android开发中也较为常用,通常作为配置类的构建器将配置的构建和表示分离开来,同时也是将配置从目标类中隔离出来,避免过多的setter方法。Builder模式比较常见的实现形式是通过调用链实现,这样使得代码更简洁、易懂,例如上文说到的ImageLoader就是通过ImageLoaderConfig进行配置,这样避免了目标类中被过多的接口“污染”。
优点
- 良好的封装性,使用建造者模式可以使客户端不必知道产品内部组成的细节。
- 建造者独立,容易扩展。
缺点
会产生多余的Builder对象以及Director 对象,消耗内存。
本文转载自《Android源码设计模式解析与实战》一书,手敲一遍,加深印象。原作者在这
